Subtotal $0.00
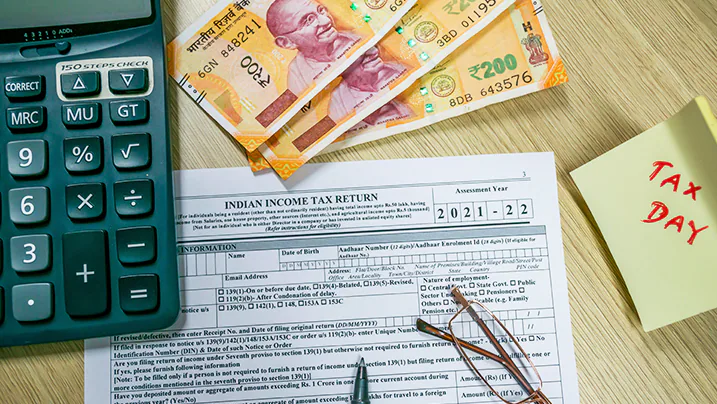
India’s 2025 Union Budget has introduced major income tax reforms aimed at salaried individuals, restructuring tax slabs to provide financial relief. These changes are designed to increase disposable income, promote savings, and enhance consumer spending, ultimately fueling economic growth. This article delves into the specifics of these revised tax slabs, their impact on salaried individuals, and the broader economic implications.
Key Changes in the Income Tax Structure
The new tax slabs have been restructured to reduce the financial burden on salaried employees, making taxation more progressive and aligned with income levels.
1. Revised Income Tax Slabs for Salaried Individuals
- Income up to ₹4 lakh – No tax
- ₹4 lakh to ₹8 lakh – 5%
- ₹8 lakh to ₹12 lakh – 10%
- ₹12 lakh to ₹16 lakh – 15%
- ₹16 lakh to ₹20 lakh – 20%
- ₹20 lakh to ₹24 lakh – 25%
- Above ₹24 lakh – 30%
This revision in tax slabs aims to reduce the tax burden on lower and middle-income earners while ensuring fair contributions from high-income groups.
2. Increased Tax Exemption Limit
To provide greater financial relief, the tax exemption threshold has been increased from ₹7 lakh to ₹12 lakh. This means that individuals earning up to ₹12 lakh will not have any tax liability, ensuring higher disposable income for personal and household expenses.
3. Enhanced Standard Deduction
The standard deduction for salaried individuals and pensioners has been raised from ₹50,000 to ₹75,000, further reducing taxable income. This move directly benefits employees, retirees, and pensioners, helping them manage their finances more effectively.
Impact on Salaried Individuals
The new tax reforms are expected to bring multiple benefits to salaried individuals, easing financial stress and providing more avenues for savings and investments.
1. Increased Disposable Income
With lower tax rates and higher exemption limits, salaried employees will have more money in hand after tax deductions. This additional income can be used for personal expenses, lifestyle improvements, or future investments.
2. Encouragement of Savings and Investments
By reducing tax liabilities, the government encourages salaried professionals to save and invest in various financial instruments such as:
- Provident Fund (PF) contributions
- Fixed Deposits (FDs)
- Mutual Funds
- Life Insurance Policies
- Real Estate Investments
3. Boost in Consumer Spending
Higher disposable income is likely to result in increased spending on goods and services, benefiting industries like:
- Retail and E-commerce
- Automobile sector
- Tourism and Hospitality
- Real Estate and Housing
This surge in consumer spending can stimulate economic activity and create more employment opportunities.
Economic Implications of the New Tax Structure
The restructuring of tax slabs and increased standard deductions are not just beneficial for individuals but also have wider economic implications.
- Stronger Middle-Class Growth – With more money available for savings, investments, and spending, India’s middle class is expected to expand and drive economic progress.
- Higher Financial Inclusion – More people may start investing in formal financial products, leading to better financial security.
- Revenue Considerations for the Government – While tax cuts benefit individuals, the government may need to balance revenue losses by increasing compliance and reducing tax evasion.
Expert Opinions on the New Tax Slabs
Economic experts and financial analysts have responded positively to the 2025 budget tax reforms, calling them a game changer for India’s salaried professionals.
- Financial strategists believe that these changes will help individuals achieve better financial planning and stability.
- Market analysts predict higher economic activity due to the increased spending power of the middle class.
- Tax consultants emphasize that individuals should now reassess their investment portfolios to maximize benefits from the revised slabs.
Challenges and Considerations
While the new tax structure is a step forward, it also presents certain challenges that must be addressed:
- Potential Fiscal Deficit Impact – Lower tax rates could reduce government revenue, requiring compensatory measures like increased compliance and alternative revenue streams.
- Inflationary Concerns – Higher consumer spending might contribute to inflationary pressures in some sectors.
- Need for Simplification – While the tax slabs have been revised, further simplification of the tax filing process can enhance compliance and ease the burden on taxpayers.
Conclusion
India’s 2025 Union Budget tax reforms mark a progressive shift in the country’s tax structure, providing major relief to salaried individuals. With lower tax rates, increased exemption limits, and higher standard deductions, taxpayers can save more, invest better, and spend efficiently. While the government faces the challenge of balancing economic growth with revenue generation, these reforms are expected to benefit individuals and the broader economy in the long run.